DEFINATION:
Its a Combination of marketing elements used in the sale of a particular product.The tools available to a business to gain the reaction which it is seeking from its target market in relation to its marketing objectives.
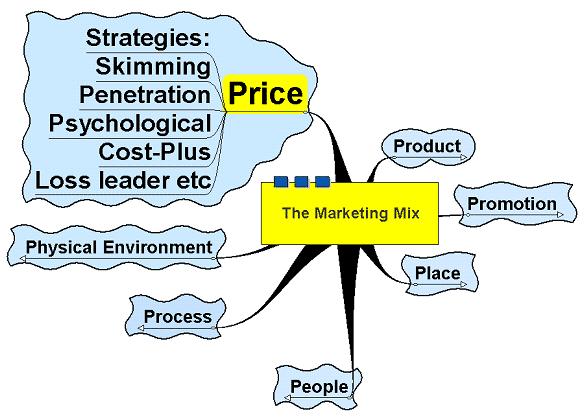
It consists of 7Ps – Price, Product, Promotion, Place, People, Process, Physical Environment.
Traditional 4Ps are extended to encompass growth of service industry.
Pricing Strategies:
There are many ways to price a product. Let's have a look at some of them and try to understand the best policy/strategy in various situations. Premium pricing, penetration pricing, economy pricing, and price skimming are the four main pricing policies/strategies. They form the bases for the exercise. However there are other important approaches to pricing.
Price Skimming:
Charge a high price because you have a substantial competitive advantage. However, the advantage is not sustainable. The high price tends to attract new competitors into the market, and the price falls due to increased supply. Manufacturers of digital watches used a skimming approach in the 1970s. Once other manufacturers were tempted into the market and the watches were produced at a lower unit cost and other marketing strategies and pricing approaches are implemented. E.g. mobilink
Penetration Pricing:
The price charged for products and services is set artificially low in order to gain market share. Once this is achieved, the price is increased. This approach was used by France Telecom and Sky TV. E.g. telenor
Psychological Pricing:
This approach is used when the marketer wants the consumer to respond on an emotional, rather than rational basis. For example 'price point perspective' 99 cents not one dollar.
Cost-plus pricing:
Cost-plus pricing is the simplest pricing method. The firm calculates the cost of producing the product and adds on a percentage (profit) to that price to give the selling price. This method although simple has two flaws; it takes no account of demand and there is no way of determining if potential customers will purchase the product at the calculated price.
Price = Cost of Production + Margin of Profit.
Loss Leader: Basic Concept In the majority of cases, this pricing strategy is illegal under EU and US Competition rules. No market leader would wish to sell below cost unless this is part of its overall strategy. The idea of selling at a loss may appear to be in the public interest and therefore not often challenged. Only when the leader pushes up prices, it then becomes suspicious.
Product:
For many a product is simply the tangible, phsysical entity that they may be buying or selling. You buy a new car and that's the product - simple! Or maybe not. When you buy a car, is the product more complex than you first thought? In order to actively explore the nature of a product further, lets consider it as three different products - the CORE product, the ACTUAL product, and finally the AUGMENTED product.The CORE product is NOT the tangible, physical product. You can't touch it. That's because the core product is the BENEFIT of the product that makes it valuable to you. So with the car example, the benefit is convenience i.e. the ease at which you can go where you like, when you want to. Another core benefit is speed since you can travel around relatively quickly.
The ACTUAL product is the tangible, physical product. You can get some use out of it. Again with the car example, it is the vehicle that you test drive, buy and then collect.
The AUGMENTED product is the non-physical part of the product. It usually consists of lots of added value, for which you may or may not pay a premium. So when you buy a car, part of the augmented product would be the warranty, the customer service support offered by the car's manufacture, and any after-sales service.
Extension Strategies
Businesses will attempt to use extension strategies to prevent their product from going into decline. They will have to spend money in research and development to try and retain periods of growth and maturity for as long as possible in order to maximise sales.Specialized versions:
For example Suzuki baleno sports.
New editions:
For example new editions of different softwares like antivirus , etc.
Changed packaging:
For example Pepsi
Promotion:
It is the communication link between sellers and buyers for the purpose of influencing, informing or persuading a potential buyer's purchasing decision.
A successful product or service means nothing unless the benefit of such a service can be communicated clearly to the target market. An organisations promotional strategy can consist of:
Advertising: It is any non personal paid form of communication using any form of mass media.
Direct Mail: Is the sending of publicity material to a named person within an organisation. There has been a massive growth in direct mail campaigns.
Organisations can pay thousands of pounds for databases, which contain names and addresses of potential customers.
Direct mail allows an organisation to use their resources more effectively by allowing them to send publicity material to a named person within their target segment. By personalising advertising, response rates increase thus increasing the chance of improving sales.
Special offers: Special offers are made for promotional purposes.e.g
— percentage reductions of the travel price,
— early booking discounts ,
— reductions for elderly persons and families.
Endorsement: In promotion, endorsement consists of :
— a written or spoken statement,
— sometimes from a person figure,
— sometimes from a private citizen, extolling the virtue of some product.
E.g: Shahid Afridi in head n shoulders advertisment.
User trials: User trials are also used for promotion purposes. Setting up a user trial is primarily about creating an environment that enables the interaction between a product and a user.It may the consumer to check the product and its usability.
Direct mailing: Is the sending of publicity material to a named person within an organisation. There has been a massive growth in direct mail campaigns. Organisations can pay thousands of pounds for databases, which contain names and addresses of potential customers.
Promotion Strategies make the consumer aware of the existence of a product or service NOT just advertising.
Placement:
Placement under marketing mix involves all company activities that make the product available to the targeted customer (Kotler and Armstrong, 2004). Based on various factors such as sales, communications and contractual considerations, various ways of making products available to customers can be used (Lazer, 1971). Companies such as Ford, Ferrari, Toyota, and Nissan use specific dealers to make their products available, whereas companies such as Nestle involve a whole chain of wholesaler retailers to reach its customers. On a general note, while planning placement strategy under marketing mix analysis, companies consider six different channel decisions including choosing between direct access to customers or involving middlemen, choosing single or multiple channels of distributions, the length of the distribution channel, the types of intermediaries, the numbers of distributors, and which intermediary to use based on the quality and reputation.
Retail: To sell in small quantities directly to consumers. Retailers will have a much stronger personal relationship with the consumer. The retailer will hold several other brands and products. A consumer will expect to be exposed to many products. Products and services are promoted and merchandised by the retailer. The retailer will give the final selling price to the product. Retailers often have a strong 'brand' themselves e.g. Ross and Wall-Mart in the USA.
Wholesale: They break down 'bulk' into smaller packages for resale by a retailer. They buy from producers and resell to retailers. They take ownership or 'title' to goods whereas agents do not. They provide storage facilities. For example, cheese manufacturers seldom wait for their product to mature. They sell on to a wholesaler that will store it and eventually resell to a retailer. Wholesalers offer reduce the physical contact cost between the producer and consumer e.g. customer service costs, or sales force costs. A wholesaler will often take on the some of the marketing responsibilities. Many produce their own brochures and use their own telesales operations.
Internet: The Internet has a geographically disperse market. The main benefit of the Internet is that niche products reach a wider audience. Use e-commerce technology (for payment, shopping software, etc).
Direct selling: Direct selling is a retail channel for the distribution of goods and services. It may be defined as marketing and selling products, direct to consumers away from a fixed retail location. The direct personal presentation, demonstration, and sale of products and services to consumers, usually in their homes or at their jobs.
Peer to peer: It is a technique of encouraging customers to promote the product to one another. Multi-channel: Multi-channel marketing utilizes many different marketing channels to reach a customer. It helps in reaching customers by: direct mail,text messaging, web sites, e-mail, door to door campaigns, newspaper advertisements.
Mail order: The other way through which product can reach the consumer includes mail order. Mail order is a term which describes the buying of goods or services by mail delivery. The buyer places an order for the desired products with the merchant through some remote method such as through a telephone call or web site. Then, the products are delivered to the customer.
The 4 Cs: Many now dismiss the four Ps as being out of date and have developed the four Cs to replace that concept.
Place becomes Convenience.
Price becomes Cost to the user.
Promotion becomes Communication.
Product becomes Customer needs and wants.
The four C's reflect a more customer oriented marketing philosophy. They provide useful reminders that you need to focus entirely on the customer when deciding where to offer a service.




No comments:
Post a Comment